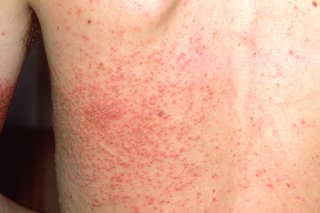
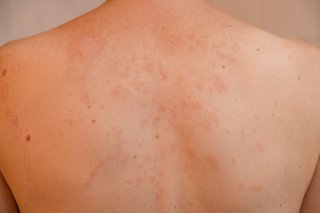
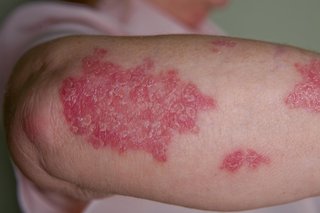
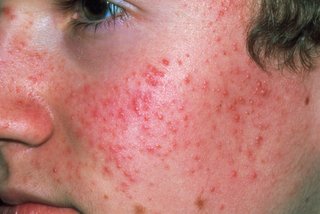
If your skin breaks out in bumps or patches you may have a rash. These patches can look red on white skin and grey on black or brown skin.
If the rash appeared quickly and you do not feel well, you may have an infection.
If you have a rash but feel well, it is probably an allergic reaction to something. The most common type of allergic reaction is urticaria (hives).
It can also mean your skin has come into contact with something that has caused a reaction.
Types of rashes These can include hives, heat rashes or long term skin conditions such as psoriasis.
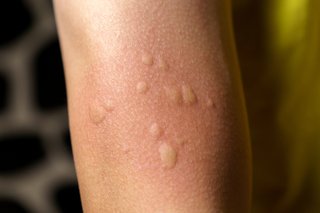
Hives A hives rash can come in patches in many shapes and sizes.
Hives are raised, itchy bumps on your skin that appear like a rash.
Many things can trigger hives. These include:
Check if you have hives
Heat rash A heat rash is uncomfortable, but usually harmless. It usually gets better on its own after a few days.
The symptoms of a heat rash are:
small, raised spots an itchy, prickly feeling mild swelling The rash often looks red, but this may be less obvious on brown or black skin. It can appear anywhere on the body.
It can appear anywhere on the body and spread, but it cannot be passed on to other people.
Heat rash appears as raised spots that are 2mm to 4mm across. Some spots may be filled with fluid.
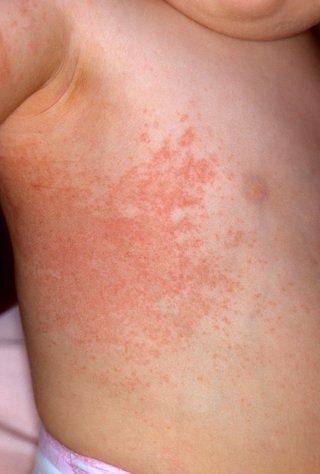
Rashes in children A rash on your child’s skin can be caused by a number of things.
These include:
Photos of rashes Check your or your child's rash against these common rashes.
Rashes common in children
Some rashes are common in children. They include:
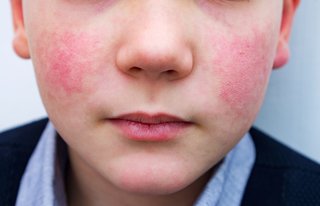
Slapped cheek syndrome
In slapped cheek syndrome, after 1 to 3 days, a bright red rash appears on both cheeks. Adults do not always get the rash.
Slapped cheek syndrome
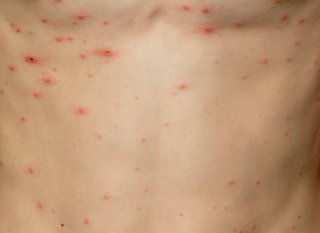
Chickenpox
Chickenpox starts with red spots. They become very itchy after about 12 hours.
Chickenpox
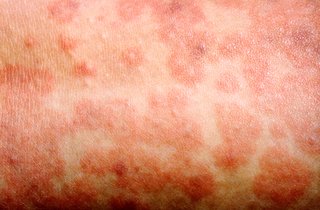
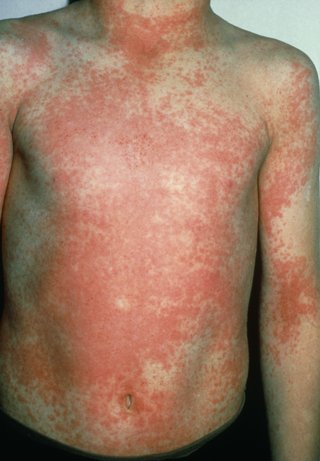
Measles
The measles rash appears around 2 to 4 days after the first symptoms.
Measles
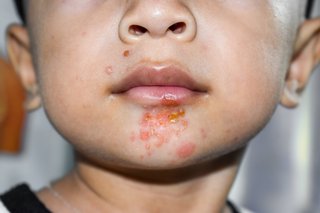
Impetigo
With impetigo, sores (non-bullous impetigo) or blisters (bullous impetigo) can start anywhere - but usually on exposed areas like your face and hands.
Impetigo
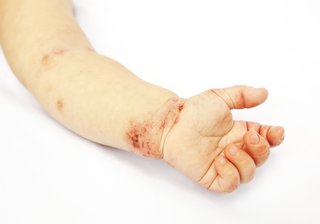
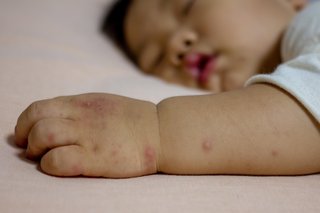
Eczema
Baby with eczema on their arm.
Eczema
Skin conditions with a rash
Some skin conditions where you will have a rash include:
Scabies
The rash spreads and turns into tiny red spots.
Scabies
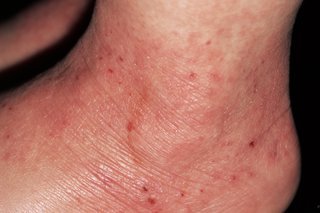
Contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis causes the skin to become itchy, blistered, dry or cracked.
Contact dermatitis
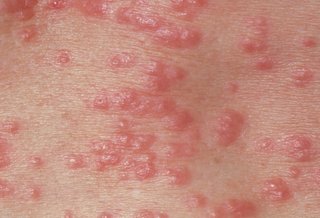
Pityriasis rosea
Pityriasis rosea causes a temporary rash of raised red scaly patches on the body.
Pityriasis rosea
Rashes which last for more than 2 weeks
Psoriasis
Plaque psoriasis (psoriasis vulgaris)
Psoriasis
Acne
Acne causes spots, oily skin and sometimes skin that's hot or painful to touch
Acne
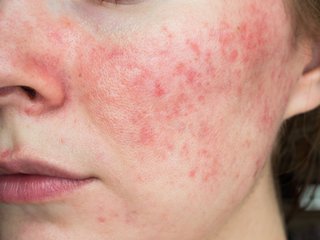
Rosacea
1 of the first signs of rosacea is redness (blushing) across your nose, cheeks, forehead and chin that comes and goes. It may be harder to see on black or brown skin.
Rosacea
Eczema
Eczema causes areas of skin to become itchy, dry, cracked, sore and red
Eczema
Rashes caused by infections
If you feel ill and you have a rash, it is more likely that you have an infection.
Common infections with a rash include:
Chickenpox Chickenpox starts with red spots. They can appear anywhere on the body.
Chickenpox starts with red spots. They can appear anywhere on the body.
Chickenpox symptoms
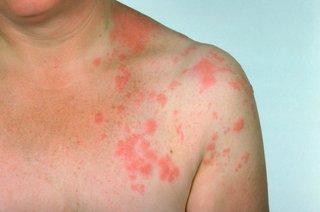
Shingles The shingles rash appears as red blotches on your skin, on one side of your body only. A rash on both the left and right of your body is unlikely to be shingles.
The shingles rash appears as red blotches on your skin, on one side of your body only. A rash on both the left and right of your body is unlikely to be shingles.
Shingles symptoms
Measles The measles rash appears around 2 to 4 days after the first symptoms.
Symptoms of measles
Hand, foot and mouth disease
Hand, foot and mouth disease symptoms
Scarlet fever
Check if you have scarlet fever
Rashes caused by fungal infections
Some rashes are caused by fungal infections such as:
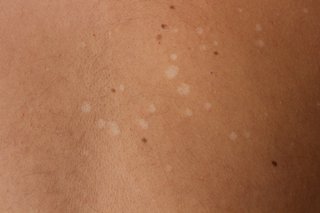
Pityriasis versicolor
Pityriasis versicolor causes small patches of skin to become scaly and discoloured.
Pityriasis versicolor symptoms
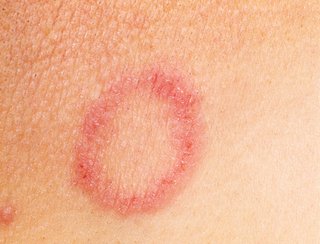
Ringworm
The main symptom of ringworm is a red or silver rash. The rash may be scaly, dry, swollen or itchy.
Symptoms of ringworm
Rashes caused by bacteria
Bacteria can also cause rashes such as:
Impetigo Impetigo is a skin infection that is very contagious but not usually serious.
Impetigo starts with red sores or blisters. They burst and leave crusty, golden-brown patches.
Symptoms of impetigo
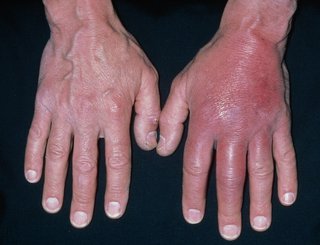
Cellulitis Cellulitis is a common bacterial skin infection that's treated with antibiotics. It can be serious if it's not treated.
Cellulitis is a common bacterial skin infection that's treated with antibiotics. It can be serious if it's not treated.
Symptoms of cellulitis
Treatment for rashes Antibiotics do not help most rashes.
Hives are usually treated with antihistamine tablets. Ask your pharmacist for advice. You can also take paracetamol or ibuprofen if you have any pain.
Put on an emollient and wash with a non-fragranced and soap-free cleanser.
Treating itchy skin
Non-urgent advice: Go to your GP if:
you have a rash and do not feel well They can check if an infection is causing the problem. Some infections caused by viruses may need treatment.