Eating a wide variety of nourishing foods gives you the energy and nutrients you need to stay healthy.
Benefits of eating healthily
Eating well helps you feel your best and can reduce your chance of developing certain diseases.
If you have children, you’re also more likely to pass on good eating habits to them.
Good eating habits can help you to have:
- a healthier body weight
- a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease and cancer
- a healthy cholesterol level
- an improved sense of wellbeing
Good eating habits can also support you to live well with health conditions, such as:
- obesity
- type 2 diabetes
- long COVID
- heart disease
Diet, nutrition and your body
Foods are made up of nutrients. Protein, carbohydrate, fat, vitamins and minerals are types of nutrients.
Your body needs the right mix of nutrients to be healthy and well. This is what it means to eat a balanced diet.
Different foods contain different nutrients. Choosing a mix of foods every day will help you get to get all the nutrients you need.
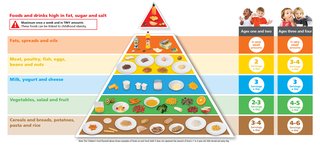
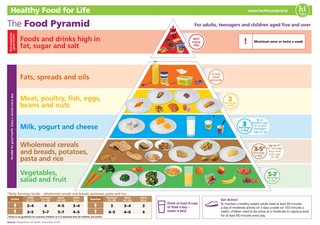
Foods that contain the same types of nutrients are grouped together in the food pyramid as:
- vegetables, salads and fruit
- wholemeal cereals and bread, potatoes, pasta and rice
- milk, yogurt and cheese
- lean meat, poultry, fish, eggs, beans and nuts
- fats, spreads and oils
If you do not get enough nutrients in your diet, you may be at risk of malnutrition.
Vitamins and minerals
Vitamins and minerals are nutrients your body needs in small amounts to work properly and stay healthy.
Most people should get all the nutrients they need by having a varied and balanced diet. But some people may need to take extra supplements.
More about minerals and vitamins
Healthy eating habits
How you plan and prepare your food and drinks can make a difference to your health.
Plan your eating habits using these tips:
- Eat regular meals and snacks.
- Plan your meals in advance - this helps you eat a variety of nutritious foods and save money by having less convenience and processed foods
- Prepare your meals using mostly fresh ingredients and choose foods like fruits, salads and vegetables for snacks.
- Use healthier cooking methods like grilling and steaming instead of frying or roasting with oil or fat.
- Use the food pyramid as a guide for serving sizes.
- Take time to enjoy your meals sitting at a table.
- Avoid eating in front of TV or computer screens.
- Ask your GP if the "Healthy Food Made Easy" course is available near you.
- To limit food waste, use leftovers in meals or snacks the next day.
Make healthy choices
Use the food pyramid as a guide for the types and amounts of food you need each day.
The number of servings you need depends on:
- your age
- your size
- if you are a man or a woman
- your activity levels
The nutrition advice for babies and children aged 0 to 4 years is different to that for older children and adults.
Learn more about nutrition for babies and young children aged 0 to 4
Food pyramid for 0 to 4 year olds
Food pyramid for people aged 5 and older
The food pyramid overview (Video)
Vegetables, salads, fruits
Base your meals on plenty of vegetables, salads and fruits. They provide many important vitamins, minerals and fibre.
Fill half your plate with vegetables, salads or fruit at every meal. Choose a variety of colours.
Choose 5 to 7 servings a day.
Serving size
One serving size is:
- 1 apple, orange, pear or banana
- 2 plums, kiwis or mandarin oranges
- 6 strawberries
- 10 grapes
- 16 raspberries
- half a cup of cooked vegetables - fresh or frozen
- 1 bowl of salad – lettuce, tomato, cucumber
- 1 bowl of homemade vegetable soup
- 150ml of unsweetened fruit juice
Add fresh or frozen vegetables to stir-fries, stews and curries.
Limit fruit juice to once a day with a meal and always choose unsweetened.
Wholemeal cereals and breads, potatoes, pasta and rice
Choose wholemeal and wholegrain breads, cereals, pasta and brown rice.
Wholegrain and wholemeal choices contain vitamins and fibre to help keep your digestive system healthy.
Wholemeal breads, cereals and potatoes provide the best energy for the body to work.
Choose a variety of foods from this shelf every day
Serving size
One serving size is:
- 2 thin slices of wholemeal bread
- 1.5 slices of wholemeal soda bread
- 1 pitta
- a third of a cup of dry porridge oats
- half a cup of unsweetened muesli
- 1 cup of flaked type breakfast cereal
- 1 cup of cooked rice, pasta, noodles or couscous
- 2 medium or 4 small potatoes
- 1 cup of yam or plantain
Milk, yogurt and cheese
Choose low-fat milk, yogurt or cheese. Low-fat options have the same amount of calcium as full fat.
Choose milk and yogurt more often than cheese.
These foods provide us with protein and calcium, which is important for healthy bones and teeth.
Serving size
One serving size is:
- 1 glass (200ml) milk
- 1 carton (125g) yogurt
- 1 bottle (200ml) yogurt drink
- 2 thumbs (25g) of hard or semi‑hard cheese, such as cheddar or edam
- 2 thumbs (25g) soft cheese, such as brie or camembert
Using milk in cereal can be a good way to reach 5 servings a day for children.
Some yogurts and yogurt drinks can have added sugar. Check the label.
If you choose dairy alternatives such as soya milk and yogurts, choose the ones that have added calcium.
Meat, poultry, fish, eggs, beans and nuts
Include a variety of lean meat, fish, poultry, eggs, nuts or beans in 2 meals per day. Choose fish up to twice a week - one of these should be oily fish, such as salmon or mackerel.
These foods provide an important source of protein. Lean red meat is also a good source of iron.
Limit how often you eat processed meats.
Use low-fat cooking methods such as grilling, baking, steaming or boiling.
Serving size
One serving size is:
- 50g to 75g of cooked lean beef, lamb, pork, mince or poultry (half the size of the palm of your hand)
- 100g of cooked fish, soya or tofu
- three quarters of a cup of beans or lentils
- 2 eggs
- 40g of unsalted nuts or seeds
Fats, spreads and oils
A small amount of fat is an essential part of a healthy, balanced diet. Fat is a source of essential fatty acids, which the body cannot make itself.
The main types of fat found in food are:
- saturated fats
- unsaturated fats
Most fats and oils contain saturated and unsaturated fats in different amounts.
Try to cut down on foods and drinks that are high in saturated fats and replace some of them with unsaturated fats.
Serving size
One serving is:
- 1 portion pack of reduced-fat or light spread for 2 slices of bread
- 1 teaspoon per person of rapeseed, olive, canola, sunflower or corn oil used in cooking
Food and drinks high in fat, sugar and salt
Limit foods and drinks that are high in fat, sugar and salt. Eat them occasionally, but not every day.
Choose smaller amounts or fun-size servings. Limit chips and takeaway food as much as possible. Most of these are very high in fat, salt and calories.
Choose healthy snacks such as fruit and vegetables. Drink water instead of sugary drinks.
What a healthy day looks like
Find examples of how to use the food pyramid as a daily guide for healthy eating.
Tips and resources to help you eat well
Children's food pyramid: 1 to 4 year olds
Visit the safefood recipes channel on YouTube for videos to guide you in preparing a variety of healthy meals and snacks