Styes are common and should clear up on their own within a week or two. They're rarely a sign of anything serious, but may be painful until they heal.
Check if you have a stye
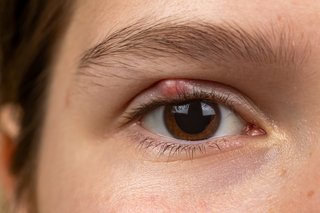
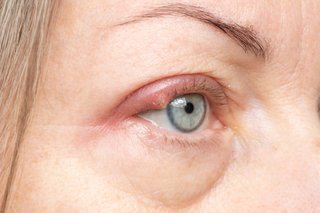
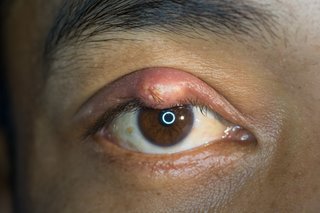
A stye usually only affects 1 eye. But it's possible to have more than 1 stye at a time.
It's probably not a stye if:
- there's no lump - if your eye or eyelid is swollen, red and watery it's more likely to be conjunctivitis or blepharitis
- the lump is hard but not very painful - it's more likely to be a chalazion
How to treat a stye
To reduce swelling and help the stye heal:
- Soak a clean face cloth in warm water.
- Hold it against your eye for 5 to 10 minutes.
- Repeat this 3 or 4 times a day.
To relieve the pain, take painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen. Do not give aspirin to children under 16.
Avoid wearing contact lenses and eye make-up until the stye has burst and healed.
Do not burst a stye
Do not try to burst a stye or remove an eyelash yourself. This can spread the infection.
Non-urgent advice: Contact a GP if your stye:
- is very painful or swollen
- does not get better within a few weeks
- affects your vision
Treatment from a GP
If you have a stye, your GP may:
- burst the stye with a thin, sterilised needle
- remove the eyelash closest to the stye
- refer you to an eye specialist in hospital
Stye prevention
You cannot always prevent a stye. Styes are often caused by bacteria infecting an eyelash follicle or eyelid gland.
Styes are not contagious. But if your eye is red, wash your hands after touching it. Do not share towels or face cloths.
You're also more likely to get a stye if you have long-term blepharitis.
You can help avoid styes by keeping your eyes clean.
Do
-
wash your face regularly
-
keep your eyelids and eyelashes clean, especially if you have blepharitis
-
remove eye make-up before bed
-
replace your eye make-up every 6 months
Don't
-
do not share towels or face cloths with someone who has a stye
-
do not rub your eyes if you have not recently washed your hands
-
do not put contact lenses in before washing your hands
Content supplied by the NHS and adapted for Ireland by the HSE