Fungal nail infections are common. They're not serious but they can take a long time to clear up.
Symptoms
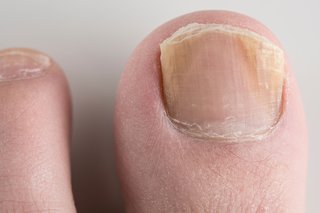
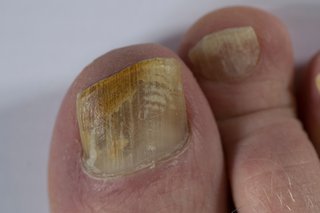
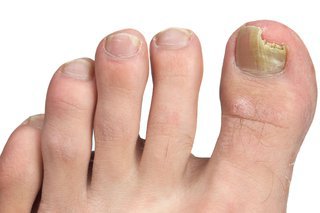
Fungal nail infections usually affect your toenails. You can get them on your fingernails too.
Fungal nail infections can make your nail:
- thicker
- change colour
- brittle
- painful
Non-urgent advice: Contact your GP, diabetes nurse or foot specialist (podiatrist) if:
- you have diabetes and have symptoms of a fungal nail infection
A foot injury or infection can lead to complications of diabetes. You are also more likely to get a fungal infection if you have a foot injury.
How a pharmacist can help with a fungal nail infection
Talk to a pharmacist if your nail is bothering you or it's painful.
They may suggest:
- antifungal nail cream - it can take up to 12 months to clear the infection and does not always work
- nail-softening cream - use for 2 weeks to soften the nail so you can scrape off the infection
When you see healthy nail growing back at the base, the infection has cleared up.
Non-urgent advice: Speak to a GP if:
- the nail infection is severe
- treatment has not worked
- the infection has spread to other nails
How a GP can help with a fungal nail infection
Your GP can prescribe antifungal tablets. You'll need to take these every day for up to 6 months.
Tablets can have side effects including:
- headaches
- itching
- loss of taste
- diarrhoea
You cannot take antifungal tablets if you're pregnant or have certain conditions. They can damage your liver.
If your nail is badly infected, you may need to have it removed. This is a small procedure done while the area is numbed (under local anaesthetic). Some GPs will do this procedure. Or they may refer you to a specialist to have the nail removed.
Causes
If you have athlete's foot, the fungus causing athlete's foot can spread to your toenails. This will cause a fungal nail infection.
You can get a fungal nail infection by:
- walking barefoot where someone with a fungal nail infection or athlete’s foot has walked, such as in changing rooms and showers
- touching your foot against the affected skin of someone with a fungal nail infection or athlete's foot
You're more likely to get it if you have wet or sweaty feet.
Preventing fungal nail infections
There are things you can do to help prevent fungal nail infections.
Do
-
treat athlete's foot as soon as possible to avoid it spreading to nails
-
keep your feet clean and dry
-
change your socks every day
-
wear flip flops in showers at the gym or pool
-
throw out old shoes
Don't
-
do not wear shoes that make your feet hot and sweaty
-
do not share towels
-
do not wear other people's shoes
-
do not share nail clippers or scissors
Content supplied by the NHS and adapted for Ireland by the HSE
