Mumps is a viral infection that spreads from person to person.
Protect your child against mumps. Make sure they get the measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) vaccine.
Symptoms of mumps
The most common symptom of mumps is painful swelling of the parotid glands. Parotid glands are salivary glands in the side of the face below the ears.
Your cheeks and jaw may be swollen.
Other symptoms of mumps include:
- a high temperature of 38 degrees Celsius or higher
- headache
- joint pain
- feeling sick
- dry mouth
- mild stomach pain
- feeling tired
- loss of appetite
These may develop a few days before the glands swell.
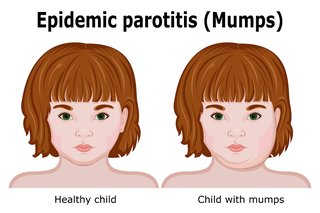
Usually both sides of the face are affected by the swelling. But sometimes only 1 side is affected. The swelling can cause pain, tenderness and difficulty with swallowing.
Sometimes mumps does not cause any noticeable symptoms.
Mumps is usually not serious. But it has symptoms similar to more serious infections such as glandular fever and tonsillitis.
Non-urgent advice: Contact your GP if:
- you think your child has mumps
Your GP can usually make a diagnosis after seeing and feeling the swelling. They will also look at your tonsils and check your temperature.
Mumps can affect other parts of your body including your brain, pancreas, testicles and ovaries.
Prevent the spread of mumps
Tell your GP you think it is mumps before you visit. They can take steps to stop the infection spreading.
Content supplied by the NHS and adapted for Ireland by the HSE